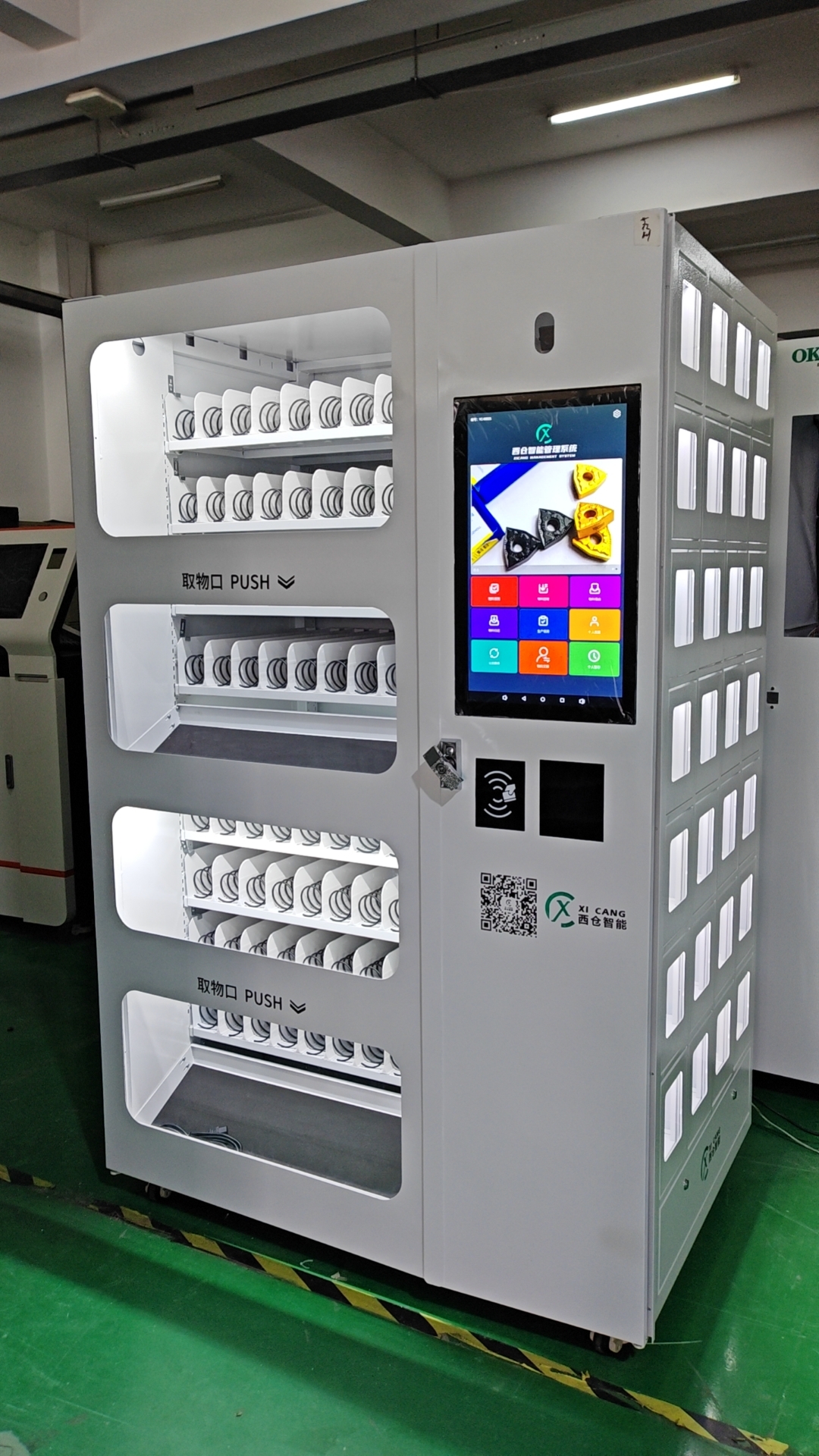
Dual Access Smart Coil & Grid Cabinet
Two dispensing ports for faster, smarter tool distribution
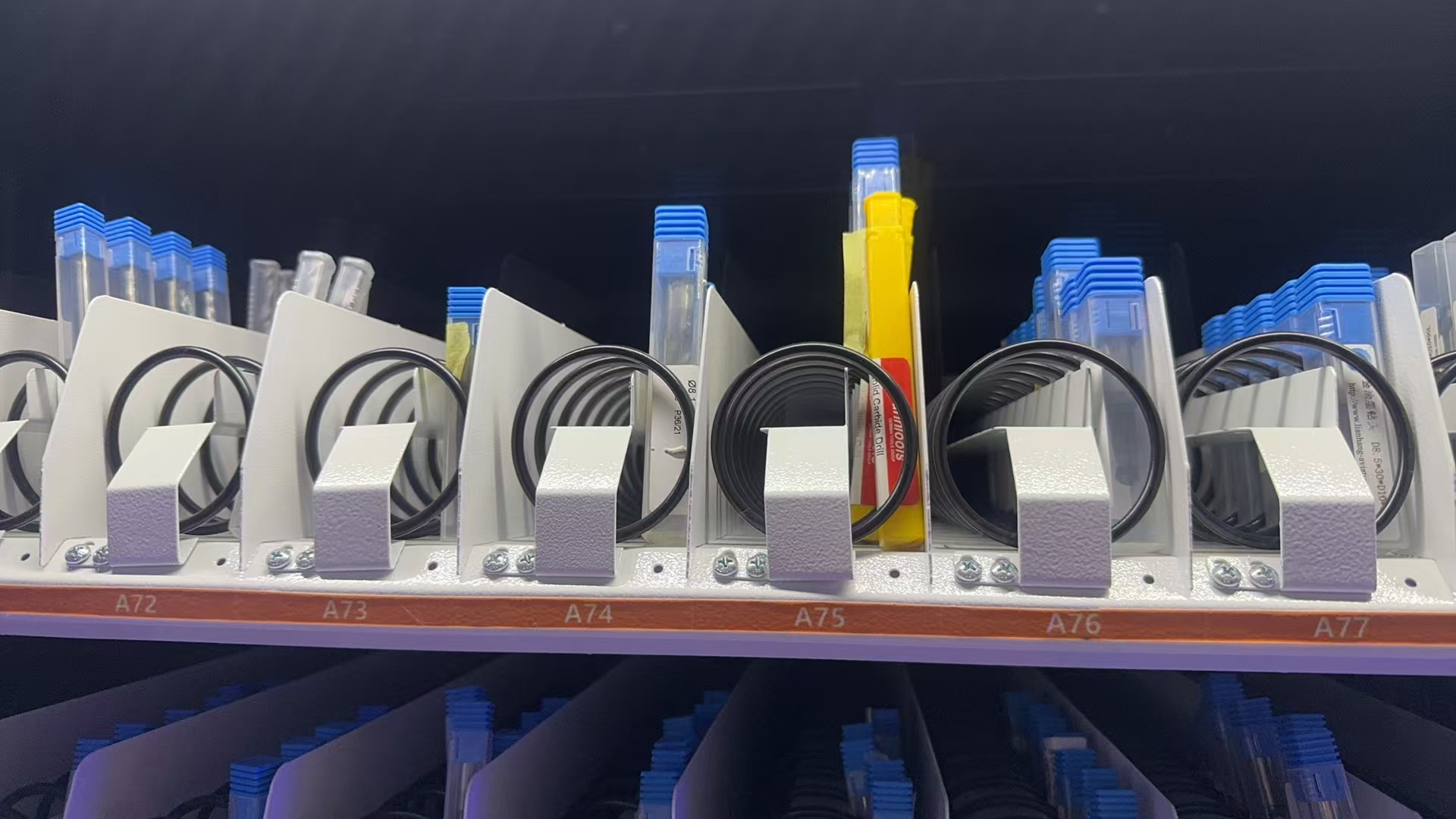
This cabinet combines spring coils and grid compartments with dual access windows, allowing two users to pick up items at the same time. It improves efficiency in busy workshops while maintaining full control over access and inventory.
Each side can be configured independently, supporting different item types such as boxed cutting tools, inserts, gloves, or small parts. With smart access control (RFID, face, code), real-time inventory tracking, and modular design, it’s ideal for factories with high tool turnover.
Applications:
CNC workshops, toolrooms, consumable management in production lines.
Highlights:
Dual user access, mixed storage modes, fast tool dispensing, customizable layout, real-time tracking.

Intelligent Workside Tool Cabinet,Intelligent Tool Handle Management Cabinet,Intelligent Labor Protection Equipment Management Cabinet,Intelligent Tool Management Cabinet
Jiangsu Xicang Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.xciwarehousing.com