This chapter introduces basic electrical engineering knowledge of photovoltaic systems. In the work of solar power generation, we inevitably need to be exposed to terms and terms related to electricity, and there are often many confusions in the use of electricity. The same components, the same way of installation, what factors lead to different power generation? Why is there a fire caused by electricity? Even if the grid-connected inverter does not work at night, why is the isolation transformer still consuming electricity? Many of the frequently-heard, seemingly simple questions that are not easily clarified will have clear answers through this chapter.
1.1, power
Everything in nature is made up of molecules. The molecules are made up of atoms. The atoms are made up of positively charged nuclei and a certain number of negatively charged electrons. Under normal circumstances, the number of positive charges carried by the nucleus is equal to the number of negative charges carried by the outer nuclear electrons, and the atoms are not electrically conductive. However, there are ways to transfer electrons from one object to another. An object that loses electrons has a positive charge, and an object that receives electrons has a negative charge. The more electrons are lost or obtained by an object, the more positive and negative charges are carried by the object.
How much of the charge that the object carries is expressed in terms of electricity use. Electricity is a physical quantity and its unit is Coulomb, which is represented by the letter C. The electricity of 1C is equivalent to the loss of the object or the amount of electricity brought by 6.25×1018 electrons.
Photovoltaic effect: The working principle of the solar cell is that solar light shines on the semiconductor pn junction to form a new hole-electron pair. Under the effect of the electric field of the pn junction, holes flow from the n region to the p region, and electrons flow from the p region to the n region. After the circuit is turned on, it forms a current.
1.2, current
The directional movement of the charge forms a current. The current has a size and direction.
1) The direction of the current: People specify that the direction in which the positive charge moves is the direction of the current. In metal conductors, the current is the result of the directional movement of electrons in the conductor under the action of an electric field. The direction of the electron flow is the direction of the movement of the negative charge, and is opposite to the direction of the movement of the positive charge, so the direction of the current in the metal conductor and the direction of the electron flow in contrast.
2) The size of the current: The magnitude of the current is measured by the current intensity in electricity. The current intensity is the amount of electricity that passes through the conductor cross section for 1 second. The current intensity is represented by letters and the formula is as follows:

In the formula I - current intensity, unit ampere (A);
Q - the amount of electricity passing through the conductor cross-section in t seconds, in Coulombs (C);
t - time, in seconds (s).
In actual use, people simply refer to current intensity as current. The unit of current is Ampere, abbreviated as Ann, denoted by letter A. If the amount of electricity passing through the conductor cross section in 1 second is 1 coulomb, the current intensity of the current is 1 ampere, and the abbreviation is 1 a. In practical applications, in addition to the unit of amps, there are thousands of amps, milliamps, and microamps. The relationship between them is:

Currents are divided into positive currents and alternating currents. Electricity from solar modules, batteries, etc. is direct current, and the current direction is constant. However, most of these household appliances cannot be used, and currents that change in size and direction over time are called currents. AC, which is our daily electricity, the frequency of the direction of change of current is called frequency, our country is 50Hz, that is, 50 changes per second, called the frequency, there are some countries for 60Hz. There are also midrange and high frequencies.
The conversion from AC to DC is called rectification. Such a device is called a rectifier. Conversely, from DC to inverter, it is called inverter. This kind of equipment is called an inverter. The PV inverter converts the DC from the PV module into a DC inverter. In the case of variable current, PV modules cannot form a loop if they are not connected to an inverter or controller. At this time, there is no current, only voltage.
1.3, voltage
The voltage is represented by the letter U, and the unit is volt. The power of the electric field force to move 1 Coulomb of charge from point a to point b is 1 Joule. Then the voltage between ab is 1 volt. For short, it is denoted by the letter V. The commonly used voltage units are kilovolts (kV), millivolts (mV), etc. The relationship between them is:
![]()
Voltage and current are similar, not only have size, but also have direction. For the load, the current flow is positive and the current flow is negative. The direction of the voltage is from the positive end to the negative end, that is to say the actual direction of the voltage in the load is consistent with the direction of the current. For DC, there are positive and negative poles. The voltage is the voltage difference between the positive and negative poles. For three-phase AC, there are phase and neutral lines. The voltage between the phase and phase lines is called the line voltage. 380Vac, the voltage between phase line and neutral line is called phase voltage, our country is 220Vac.
Photovoltaic modules have two voltages, open circuit voltage and operating voltage, such as 265W components, the operating voltage is generally 30.7V, open circuit voltage is generally 38.2V. Different component voltages are also not the same. Typically, 60-cell modules have an operating voltage of typically between 30V and 31V, and 72-cell components. The operating voltage is typically between 35V and 36V.
Common voltage: General mobile phone charger and USB power supply is 5Vdc, lead-acid batteries have 2V, 6V and 12V and other three specifications, 36Vdc is called the safe voltage below, this voltage range does not harm the human body. China's AC voltage is divided into three types, single-phase 220V, three-phase 380V called low voltage, generally for home and industrial and commercial use. Three-phase 10kV, 15kV, 35kV is called medium voltage, 110kV, 220kV, 330kV, 500kV, 1000KV is called high voltage. Different countries have different voltage levels, for example, the United States has 110V, 208V, 480V and other voltage levels, the specific reference can be found in the "Power Grid Structure and Inverter Selection of Countries in the World" article.
PV modules and inverters are grouped together. If there is sunlight, the grid-connected inverters are connected to the grid, and the off-grid inverters are connected to the load. There will be voltage and current, forming a loop. At this time, PV modules and inverters The device forms a power supply.
1.4, power supply
The power supply uses non-power to move the positive charge from the cathode to the anode, which converts other forms into electrical energy in the circuit. The electromotive force is the physical quantity that measures the energy conversion capability of the power source. It is represented by the letter E. Its unit is also volt. For short, it is denoted by the letter V.
The electromotive force of the power supply exists only inside the power supply. It is stated that the direction of the electromotive force is from the negative electrode to the positive electrode inside the power supply. In the circuit, the direction of the electromotive force is also indicated by a thin, solid line with an arrow. When the two ends of the power supply are disconnected from the load, the open circuit voltage of the power supply is equal to the electromotive force of the power supply, but the directions are opposite.
You can use the method of measuring the voltage of the component to determine whether the component is good or bad. For example, if the voltage between the positive and negative poles of the component is 35 Vdc when the sun is shining, it proves that the component is working properly. If the voltage is 0 Vdc, the component is proved. it is bad.
The power supply is divided into voltage source and current source. The off-grid inverter is a voltage source. Its characteristic is that the output voltage is kept constant and the output current changes with the load. The off-grid inverter must be equipped with a battery for normal operation because of the photovoltaic input. Unstable, unstable load, need to stabilize the voltage with the battery, when the photovoltaic input power is greater than the power of the load, the excess power into the battery storage, prevent the system voltage rise, when the photovoltaic input power is less than the load power, insufficient The electric energy is supplemented by a battery to prevent the system voltage from decreasing. The grid-connected inverter is a current source, the voltage follows the grid voltage, and the current changes following the change of the solar radiation amount and the like.
From the power supply to the load, the cable is required as a conductor to transfer electrical energy. Since the cable has resistance, it will produce a voltage drop. Therefore, although the single low voltage three-phase voltage level in China is 220/380V, the grid-connected inverter serves as the power source. Its single three-phase output rated voltage is 230/400V.
1.5, resistance
In general, the resistance of a conductor to current is called resistance and is represented by the letter R. The unit of resistance is ohms, abbreviated as Europe, and is represented by letters. If the voltage across the conductor is 1 volt and the passing current is 1 amp, the resistance of the conductor is 1 ohm.
![]()
The relationship between them is:
![]()
It should be emphasized that: The resistance is an objective existence of the conductor, it has nothing to do with the voltage changes at both ends of the conductor, even if there is no voltage, there is still a resistance in the conductor. Experiments show that when the temperature is constant, the conductor resistance is only related to the geometry of the material and the conductor. For two conductors of uniform material, length L, and cross-sectional area S, the resistance can be expressed by the following formula:

Copper and aluminum have low resistivity and are extremely widely used conductive materials. In the past, due to the abundance of aluminum deposits in China and the low price, aluminum wires were commonly used as transmission lines. Due to the better electrical properties of copper wire, such as high strength and low resistivity, copper wire is now more widely used.
Distributed photovoltaic systems DC and AC cables are generally copper or copper cables. This is due to the fact that the copper wire has less internal resistance and consumes less power.
1.6, electric power, electric power
When electrical current passes through electrical appliances, electrical energy is used to convert electrical energy into other forms of energy, such as thermal energy, light energy, and mechanical energy. We convert electrical energy into other forms that can be called current work, referred to as electrical work, denoted by the letter W. Electrical work is an instantaneous value. The unit of voltage is volts, the unit of current is safety, the unit of resistance is Europe, and the unit of time is seconds. Then the unit of electric power is joules, and abbreviated as coke, denoted by letter J. The power that a current in a unit of time passes through an electrical appliance is called electrical power, and is represented by the letter P. The electrical power is a two-dimensional value with a time axis. The power calculation method is as follows:
DC power = DC voltage * DC current. Single-phase AC power = AC voltage * AC current; three-phase AC power = line voltage * current * 1.732, such as a three-phase inverter, the output rated voltage is 400V, the output rated current is 64.5A, and the output power is 400*64.5 *1.732, which is approximately 44.7 kW.
The unit of electrical power is joules and the unit of time is seconds. The unit of electrical power is joules/sec. Joules/second is also called watts, or watts, and it is represented by the letter W. In practical work, the commonly used electric power units are kilowatts (kW) and milliwatts (mW). The relationship between them is:
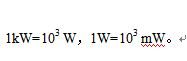
1) When the resistance of an electrical appliance is certain, the electrical power is proportional to the square of the current or the square of the voltage. If the current through the appliance is 2 times the original current, then the electrical power is 4 times the original power; if the voltage across the appliance is 2 times the original voltage, the electrical power is 4 times the original power.
2) When the current flowing through the appliance is constant, the electrical power is proportional to the resistance value. For a series resistor circuit, the current flowing through each resistor is the same, and the total power of the series resistors is proportional to the sum of the resistance values ​​of the respective resistors.
3) When the voltage applied to both ends of the appliance is constant, the electrical power is inversely proportional to the resistance. For a parallel resistor circuit, the voltages across the resistors are equal, and the electrical power of each resistor is inversely proportional to the resistance of each resistor.
In practice, the unit of electrical power is commonly used in kilowatt hours (kW•h), also called “degreeâ€. 1 kilowatt-hour is 1 degree, it means the electrical energy consumed for one hour of power consumption of 1 kilowatt, namely: 1kW • h = 1kW x 1h.
Description:Braided Packing includs many kinds such as PTFE,Graphite,Kevlar fiber,Carbon fiber etc,they are the perfect material for door seals or caulking for ovens, furnaces and boilers, expansion joints, cable or pipe wrapping, high temperature seals or gaskets. These products have been widely used in welding, foundry works, aluminum and steel mills, boiler insulation and seal, exhaust systems, shipyards, refineries, power plants and chemical plants. Braided Packing are also used as the core in tadpole gaskets. The three different styles are designed to fit different application needs: twisted rope is a soft rope, while square and round braid are more dense and solid.
PTFE Braided Packing especially suitable for sealing flange connections, pip systems, hydraulic and pneumatic systems, etc. In addition, it's a good ideal for seals in glass, enamel and plastic flanges, vessels and special shaped sealing surface.Features
Clean, non-contaminating and Long maintenance free service life
Minimal shaft wear and leakageSave money and time.



Braided Packing
Braided Packing,Non Asb Graphite Braided Packing,Flexible Graphite Braided Gland Packing,Aramid Fiber Square Braid Packing
HEBEI HENGDA SEALING MATERIALS CO.,LTD. , https://www.hengdasealing.com